Alexis Hucteau PhD project

Notes about all the project advances and researches during the PhD
Introduction
- AML
- IDH
- Where is IDHm in AML cases?
- Effects of IDHm in AML?
- Transcriptomic
- DNA Methylation
- Histone modifications
- IDHm inhibitor
- What are the actual knowledge about the inhibitor?
- IDHm inhibitor resistance
- About the resistance
- TF activities
- Different methods to infer it
- Dorothea
- i-cis Targets
- How to make it more precise?
- ATAC-seq
- Different methods to infer it
- Networks
- Inferring regulatory network?
- Different metrics
- DNA methylation
- What is it?
- What are there effects?
- How to have access to those modifications?
- Chromatin structure
- Differents states of the chromatin
- When is it modified?
- How?
- How to have access to that information?
- Single cell
- What are single cell analysis?
- To study what?
- Differentiation
- What is differentiation?
- Why is it involved in AML?
- How?
- Why is it involved in IDHm AML?
- How?
- Dedifferentiation
- What is differentiation?
- Why is it involved in AML?
- How?
- Why is it involved in IDHm AML?
- How?
- Stress response
- What is a cellular Stress?
- What is a Stress Response?
- How is it connected to AML?
- How is it connected to IDHm AML?
- Is it connected to the resistance?
AML
IDH
Mitochondrial metabolism supports resistance to IDH mutant inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia
IDH1m conferred a higher sensitivity to metformin in a transformed mammary epithelial cell line.Cuyàs et al, 2015 resulted in increased oxidative TCA metabolism under hypoxia in HCT116 colon cancer cells Grassian et al., 2014, and led to enhanced expression of genes involved in mitochondrial structure and function in cholangiocarcinoma Farshidfar et al., 2017. However, IDH1m glioma cells had reduced ATP content and respiration due to inhibition of ATP synthase or hypersuccinylation by 2-HG Fu et al., 2015; Li et al., 2015 and increased NADH-coupled proline biosynthesis, resulting in a ‘‘metabolic bypass’’ of ETC complex I Hollinshead et al., 2018.
IDH1m AML cells displayed a higher OxPHOS phenotype than WT cells without changes in mitochondrial biogenesis.
IDHm inhibitor
IDHm inhibitor resistance
Résistance Intrinsèque or primary resistance
mIDH1 inhibitor […] no significant effects were observed on altering the epigenetic state or suppression of the growth of mIDH1-containing glioma cells. x
Receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) pathway mutations
- RTK pathway mutation (for IDH1m)
- NRAS, KRAS, PTPN11, KIT, and FLT3
- JAK2 mutation (Good prognosis) –> inactive la protéine
-
Jak2 inhibition combinaison therapy with IDHm inhibitor
- NRAS subclone? (IDH2m)
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway activation
- Activation MAPK signaling pathway associated with primary resistance to IDHm Inhibition
- NRAS, PTPN11, SRSF2, ASXL1 enriched in NR
Epigenetic regulation, stemness and differentiation
- primary resistance due to leukemia stemness Leukemia stemness and co-occurring mutations drive resistance to IDH inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia
- Mutations in RUNX family transcription factor 1 (RUNX1), CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha (CEBPA), and GATA binding protein 2 (GATA2) associated with NR
- Hypermethylated phenotype (FPXC1, CD99 and DNMT3A)
- increasing stemness, which block cell differentiation and leads to the development of drug resistance.
Résistance acquise Acquired resistance
Secondary IDH mutations
Isoform switching
RTK pathway mutations
Clonal evolution and selection
Mitochondrial metabolism
Autres papiers
The Hematopoietic Oxidase NOX2 Regulates Self-Renewal of Leukemic Stem Cells
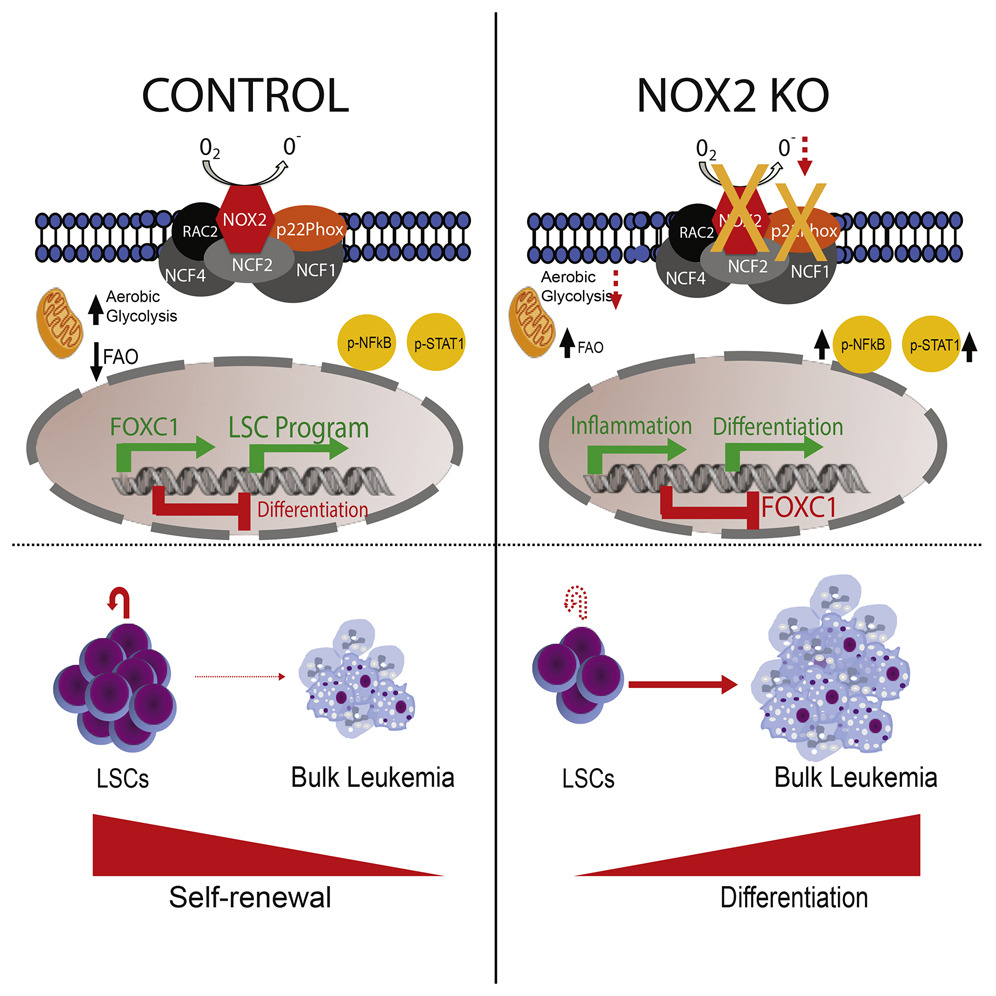
acute myeloid leukemia – leukemia stem cells – differentiation – self-renewal –glycolysis – fatty acid oxidation – NOX2 – p22Phox – ROS – FOXC1 – CEBPε – NF-κB
- Depletion of NOX2 reduces basal ROS levels and impairs core metabolism
- NOX2 regulates self-renewal- and differentiation-associated transcriptional programs
- Downstream of NOX2, FOXC1 controls part of the differentiation program
- Depletion of FOXC1 or NOX2 impairs leukemogenesis in murine models and xenografts
NOX2:
- Immune cell function
- Leukemia initiating stem cell population
- NOX2 KO –> core metabolism impaired
- NOX2 KO –>
- self-renewal program decrease
- activates inflammatory
- activates myeloid-differentiation-associated programs
forkhead transcription factor FOXC1 targets of NOX2
- Maintien des activités mito
- Co-occuring mutations NRAS MAPK pathway effectors
- no patients with mPTPN11
- mKRAS was not associated with response
- RUNX1 and FLT3
- IDHm isoform switches
- IDH2 second-site mutations
- In CR, IDHm2 leukemia cells -> Neutrophils
- may explain the lower frequency of infections in patients achieving CR with enasidenib treatment
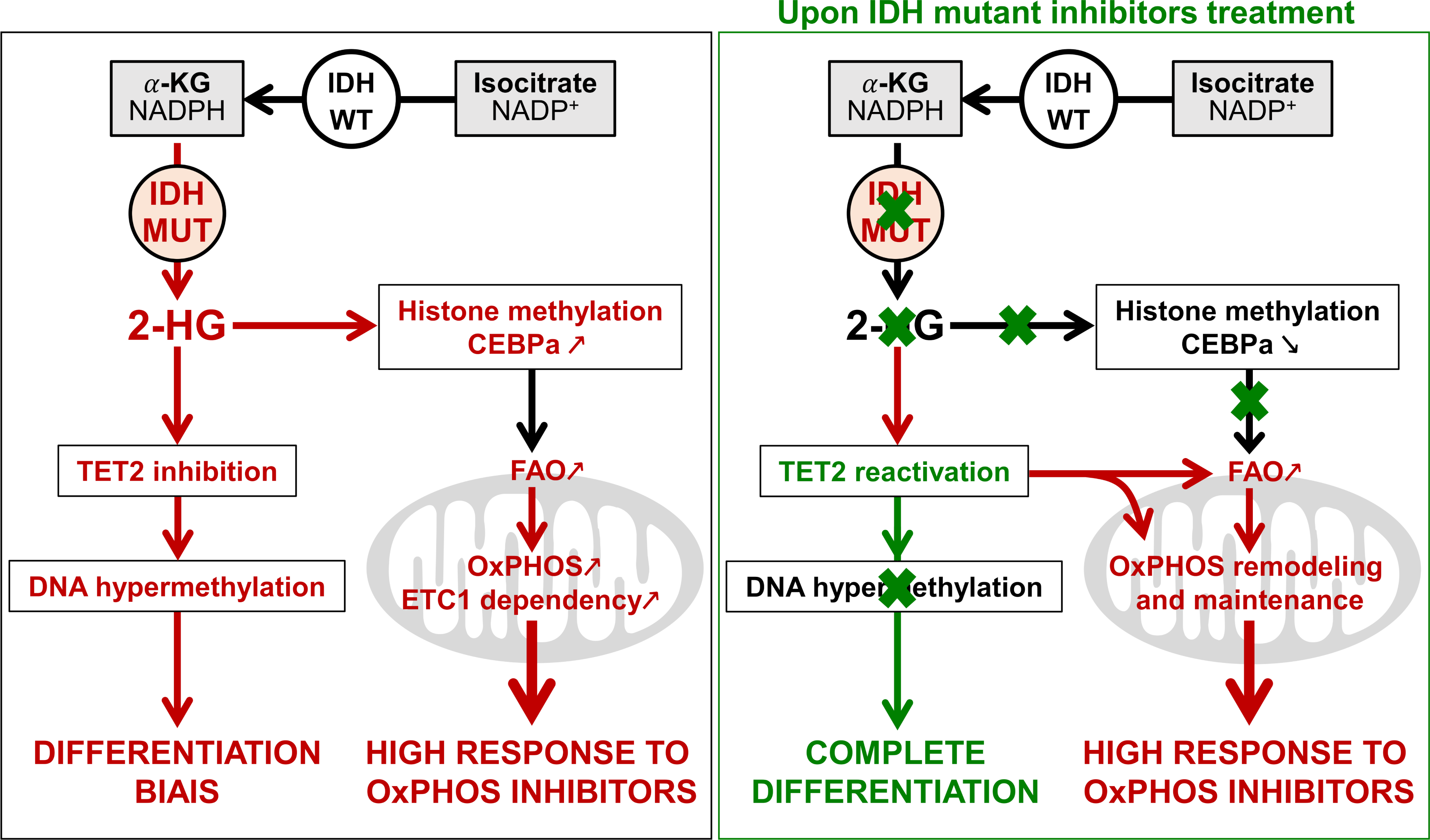
Mitochondrial metabolism supports resistance to IDH mutant inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia décrit un métabolisme mitochondrial oxydatif exacerbé. Il serait dû à une augmentation de l’expression de CPT1a via CEBPa. Malgré une réduction de l’oncométabolite 2HG via IDHmi, l’activité particulière du métabolisme est maintenue. Ce maintien serait dû à la réactivation de l’activité de TET2 et ainsi, l’expression de PTEN qui va entraîner l’inactivation d’AKT et préserver PGC1a.
Co-occurring mutations in NRAS and other MAPK pathway effectors were enriched in nonresponding patients, consistent with RAS signaling contributing to primary therapeutic resistance (https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/130/6/732/36815/Enasidenib-induces-acute-myeloid-leukemia-cell)
(https://ashpublications.org/bloodadvances/article/4/9/1894/454778/Molecular-mechanisms-mediating-relapse-following)
IDH switch isoform
Differentiation biais.
TF activities
Networks
DNA methylation
Chromatin structure
Single cell
Differentiation
Dedifferentiation
Stress response
The main topic of the thesis is in silico, epigenomic and functional investigations of resistance to IDH inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia.
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a deadly disease associated with poor outcomes. The median age of patients harbouring AML is around 70 years old and the prognoses decline with the age. For decades, intensive chemotherapies were the only treatments available. The combination of Cytarabine (AraC) and daunorubicin shows good results but not all the patients are eligible for intensive therapy. Hypomethylating agents are the current alternative therapy but only 16% of patients achieve complete remission with a median overall survival about 21 months.
Novel therapies have been accepted like the combinaison Venetoclax + Azacitidine to avoid intensive therapy but there is still a crucial need of novel therapies to overcome the relapses and refractory diseases. Although 60–80% of AML adult patients achieve complete remission after the first induction chemotherapy, roughly 20% will show primary refractory disease and more than 50% will relapse.
Specific mutations have been found to induce the relapses like FLT3-ITD, IDH1/2 or the presence of CD33 and inhibitors are already studied but there are still resistances to that therapies. IDH1 and IDH2 are metabolic genes that convert isocitrate into alpha ketoglutarate (aKG), a metabolite that is itself converted into 2 hydroxyglutarate (2HG) by the mutated IDH protein. The abnormal production of the oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) induces epigenetic and transcriptional reprogramming, differentiation bias, and susceptibility to mitochondrial inhibitors in cancer cells.
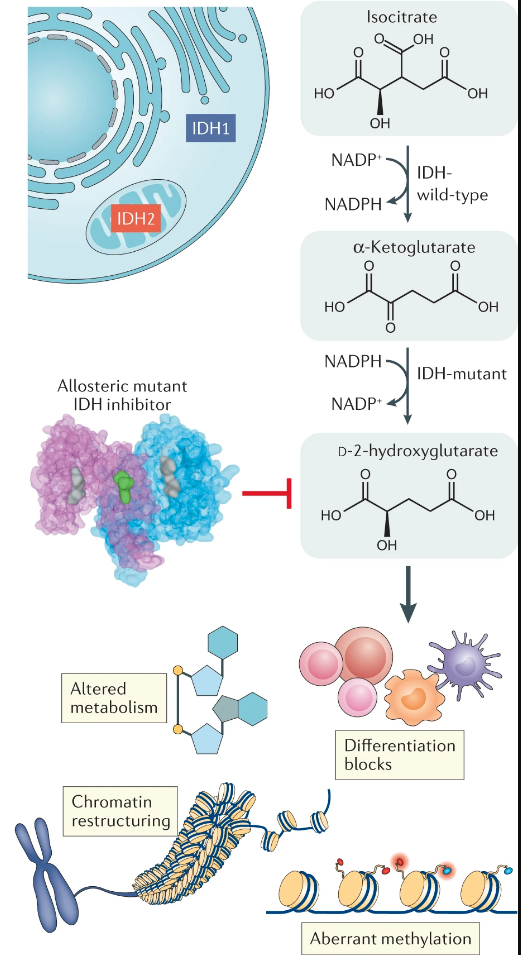
It’s important to notice that heterozygotie of IDHm is mandatory for the production of 2HG and a good balance of IDHwt protein and IDHm protein. The implications of IDH mutations for cancer development and therapy
In a recent study, it have been shown that patients with AML harboring an IDH mutation displayed an enhanced mitochondrial oxidative metabolism through the methylation-driven CEBPa induction but inhibition of the mutation, despite the reduction of CEBPa enhancement, failed to reverse the mitochondrial oxidative metabolism through an AKT/PPARGg pathway (ref: Mitochondrial metabolism supports resistance to IDH mutant inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia).
Another study from our group showed that the presence of the mutation induces Vitamin D receptor related programs priming the AML cells to differentiate with pharmacological doses of ATRA or/and VD comforting the relevance of metabolic pathway in the mutation (ref: Activation of Vitamin D Receptor Pathway Enhances Differentiating Capacity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Mutations).
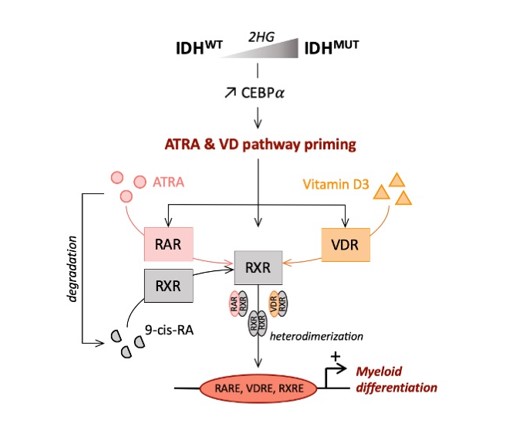
Another study focusing on the inhibition of IDH suggests that stemness is associated with primary resistance and selection of mutations in RUNX1/CEBPA or RAS/RTX pathway genes are the driver of acquired resistance (ref: Leukemia stemness and co-occurring mutations drive resistance to IDH inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia).
The IDH mutations are also studied in other cancers like in glioma. Interestingly, despite the induction of 2HG like in AML, prognosis of IDHm glioma are better than IDHwt glioma. In this study Epigenetic encoding, heritability and plasticity of glioma transcriptional cell states, they analysed scRNA-seq but also scDNAme-seq and highlight some plasticity of the cell states due to IDHmutation.

About DNA methylation in IDHm AML samples, Elisabeth R. Wilson et al. in Genome-wide analysis of focal DNA hypermethylation in IDH-mutant AML samples analyzed WGBS DNA methylation data of IDHm/wt and CD34+ cells and confirmed the importance of non-CpG island hypermethylation and more specifically of enhancer methylation. They also found an hypermethylation of an enhancer of MYC and ETV6 despite their expression changed.
To investigate the resistance, we analyzed transcriptomes of different cohorts of patients. TCGA and Verhaak datasets have been used to compare the patients samples harbouring IDH mutation to patients samples without the mutation. Verhaak data have been used to look at primary resistance through the analysis of Overall Survival and the patient cohort from Koichi’s data have been used to investigate the acquired resistance by looking at relapsed or refractory AML behaviour after IDH inhibitor therapy.
By combining transcription factor activity, differential gene expression, functional protein-protein interaction network and network analysis, we found some transcription factor like RELA, MYC, HIF1a, SMAD3 or REL that might be the main actor of the acquired resistance and STAT3/STAT4 for the primary resistance.
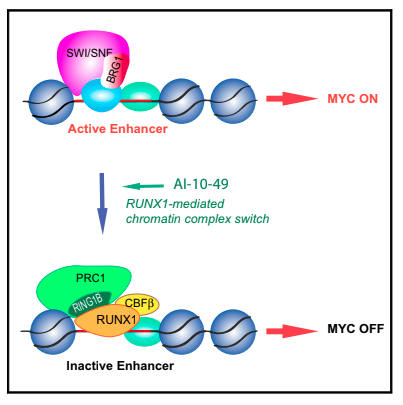
In CBFb-SMMHC Inhibition Triggers Apoptosis by disrupting MYC Chromatin Dynamics in Acute Myeloid Leukemia they showed that a chromatin alteration of the chromosome 16 leads to the repression MYC by replacing the SWI/SNF TF by RUNX1 on its enhancer.
In Integrative Genomic Analysis of Cholangiocarcinoma Identifies Distinct IDH-Mutant Molecular Profiles about Cholangiocarcinoma IDHm cases, they found a hypermethylation and downregulation of ARID1A compared to IDHwt. ARID1A is a member of the SWI/SNF family and might be link to MYC aswell.
In A Myc enhancer cluster regulates normal and leukaemic haematopoietic stem cell hierarchies, they showed a BloodENhancerCluster (BENC) enhancer region located downstream of the MYC locus is essential for HSC function
About RELA, also called NF-kB, it has been shown that it is involved in several cellular functions in hematological malignancies, i.e. inflammation, apoptosis, cell survival, proliferation, angiogenesis, and innate and acquired immunity (ref: NF-κB pathways in hematological malignancies).
But also linked to MYC as a NF-kB repressing factor (NKRF), shifted to the cytosplasm by a protein synthesis inhibitor HTT, attenuates the transactivation activity of p65 on the MYC gene (ref: Homoharringtonine deregulates MYC transcriptional expression by directly binding NF-κB repressing factor).
In AML, RELA targets a long noncoding RNA uc002jit.1. Its KO impaired the stability of PARP1, a prtein that help DNA damage repair. Its KO also inhibit AML cells proliferation and increased the sensitivity to drugs. (ref: The role of the novel LincRNA uc002jit.1 in NF-kB-mediated DNA damage repair in acute myeloid leukemia cells)
The cleavage of p65/RELA by RIP3 induces apoptosis. RIP3 silencing in leukemia cells results in suppression of the complex regulation of the apoptosis/necroptosis switch and NF-κB activity. (ref: RIP3 is downregulated in human myeloid leukemia cells and modulates apoptosis and caspase-mediated p65/RelA cleavage)
Stabilization of NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) suppresses AML. Stabilization of NIK-induced activation of NF-κB non-canonical signaling upregulates Dnmt3a and downregulates Mef2c, which suppresses and promotes AML development, respectively. Stabilization of NF-κB-Inducing Kinase Suppresses MLL-AF9-Induced Acute Myeloid Leukemia
A Myc enhancer cluster regulates normal and leukaemic haematopoietic stem cell hierarchies
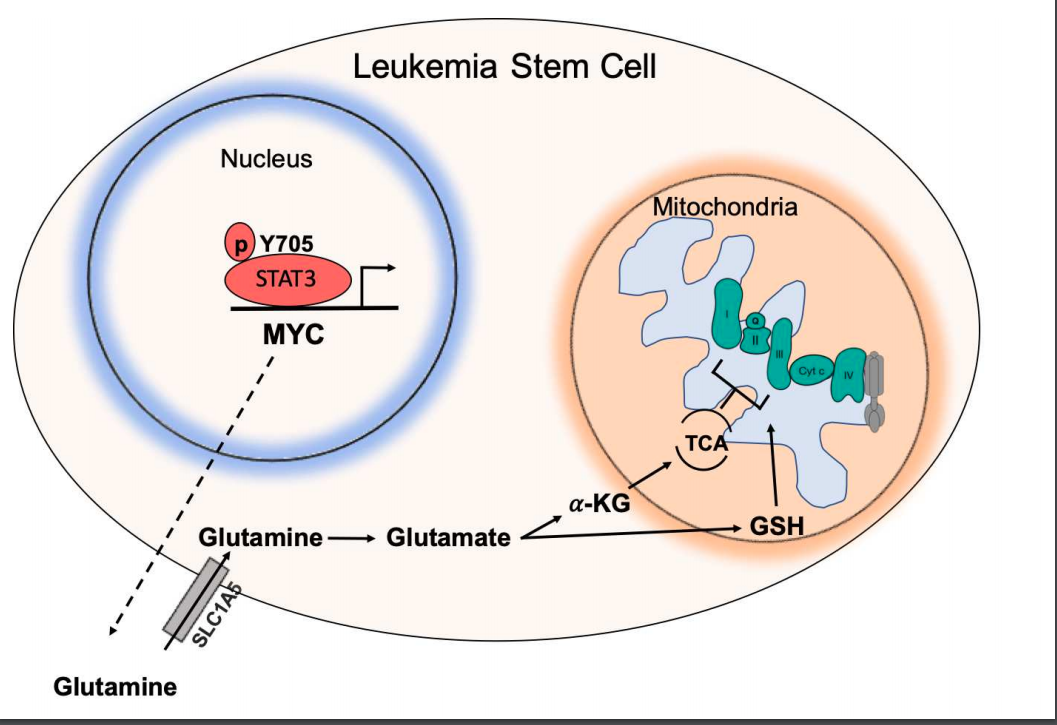
In The STAT3-MYC Axis Promotes Survival of Leukemia Stem Cells by Regulating SLC1A5 and Oxidative Phosphorylation, they characterised that STAT3 regulates amino acid influx and glutaminolysis in leukemia stem cells by promoting expression of MYC and SLC1A5 and that Depletion of glutamine and its downstream metabolites leads to a decrease in OXPHOS activity in LSCs resulting in cell death.
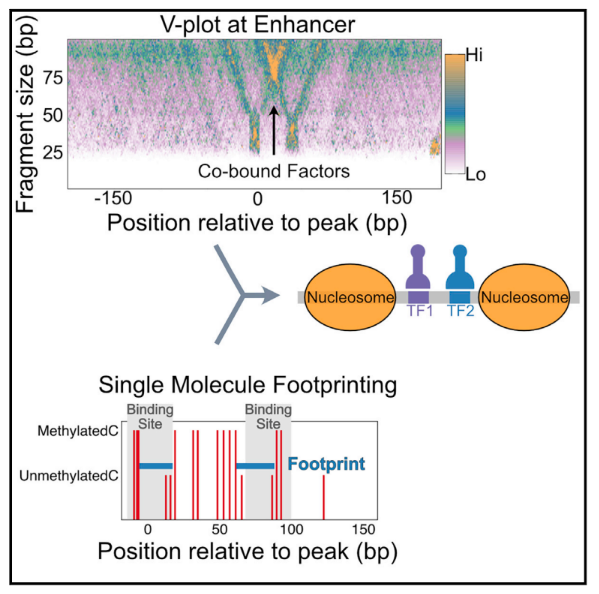
In a context of chromatin aspect, the paper Cooperative binding between distant transcription factors is a hallmark of active enhancers uncovers transcription factor binding and cooperativity at functional enhancer genome-wide in Drosophila cells. They showed that cooperativity between distanced regions imply the absence of protein-protein interaction but is driven by chromatin dynamics. The CpGs methylation is not studied here but used as experiment to find free chromatin regions.
It’s important to define one of the topic of the thesis that is stress.
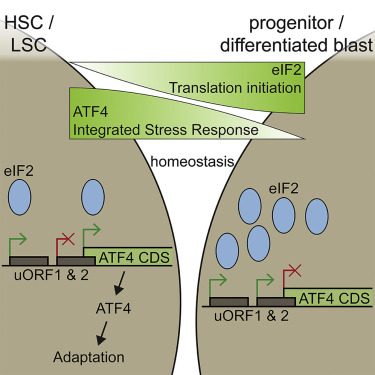
In the paper Integrated Stress Response Activity Marks Stem Cells in Normal Hematopoiesis and Leukemia, they show that AML displayed eIF2 scarcity promoting ATF4 upregulation that activates ISR promoting cell survival.
Mark S. Williams et al., in A stress-responsive enhancer induces dynamic drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia they analyzed an integrated stress response-like transcriptional program that induces ABCB1 through remodeling and activation of an ATF4-bound, stress-responsive enhancer.
to be continued